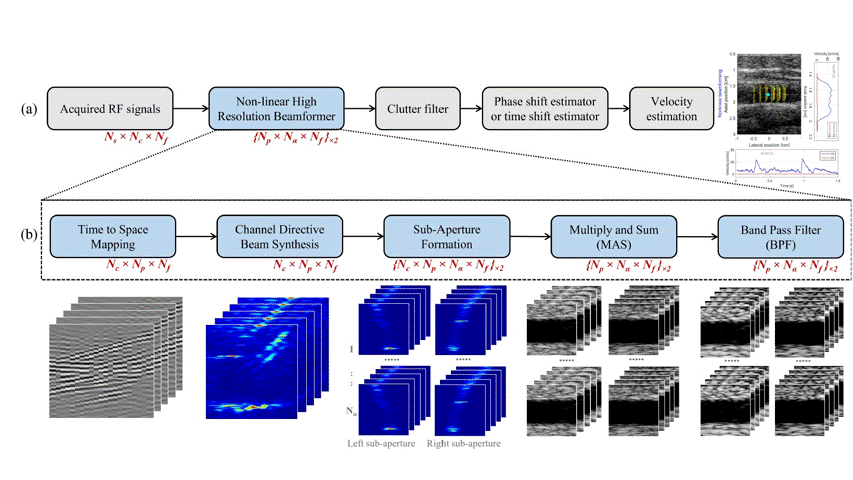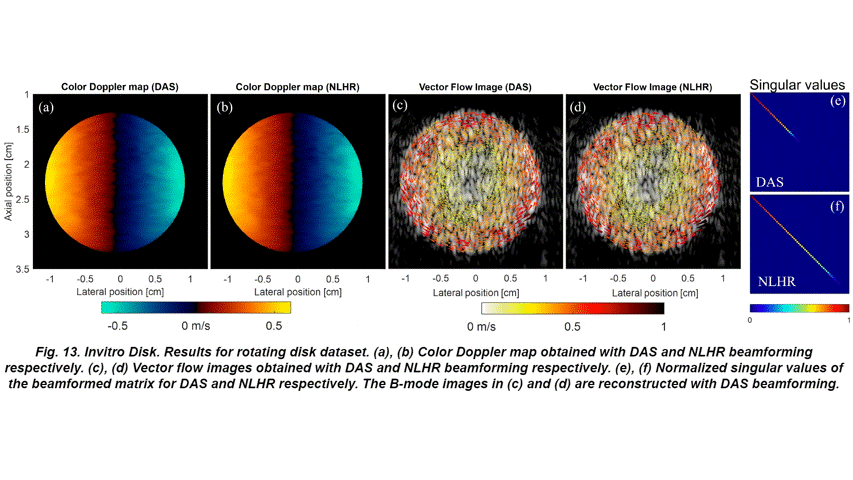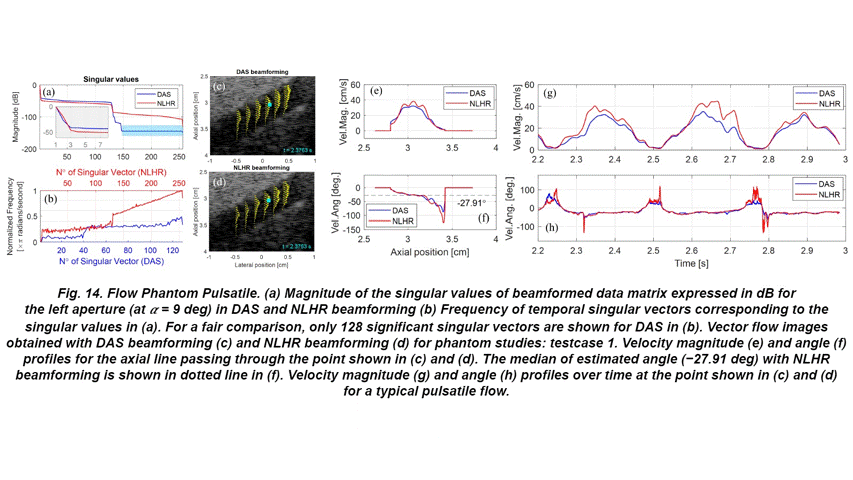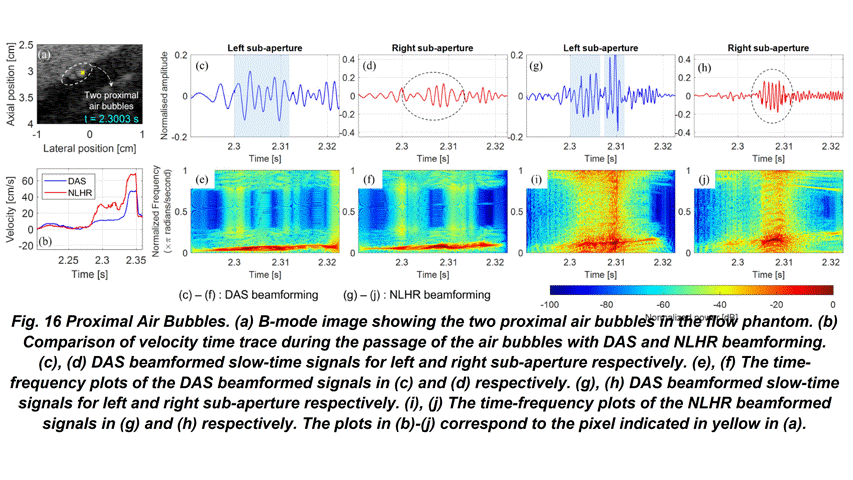
Inspired by the F-DMAS beamforming in B-mode imaging, this work attempts to address the spatiotemporal sensitivity of the conventional flow imaging techniques with a novel non-linear beamforming approach without the use of any contrast agents and deep learning based methods. The major contributions of this work are as follows.
- A novel nonlinear beamforming technique is proposed for ultrasound flow imaging and the first effort towards the application of nonlinear beamforming in flow imaging.
- We validate the proposed nonlinear beamformer using typical parabolic flow simulations with a cross-correlation based velocity estimator and an autocorrelation based velocity estimator which are the common velocity estimation techniques in the literature.
- Further, the proposed approach has been thoroughly investigated for velocity sensitivity with in-vitro datasets including a rotating disk, air bubble tracking, and flow direction reversal. Finally, we report the in-vivo performance evaluation of the proposed approach for a typical pulsatile flow in a carotid artery dataset.
- The results, when compared to the state-of-the-art DAS based flow imaging approaches, suggest that the proposed method provides better spatiotemporal sensitivity towards the flow transients.
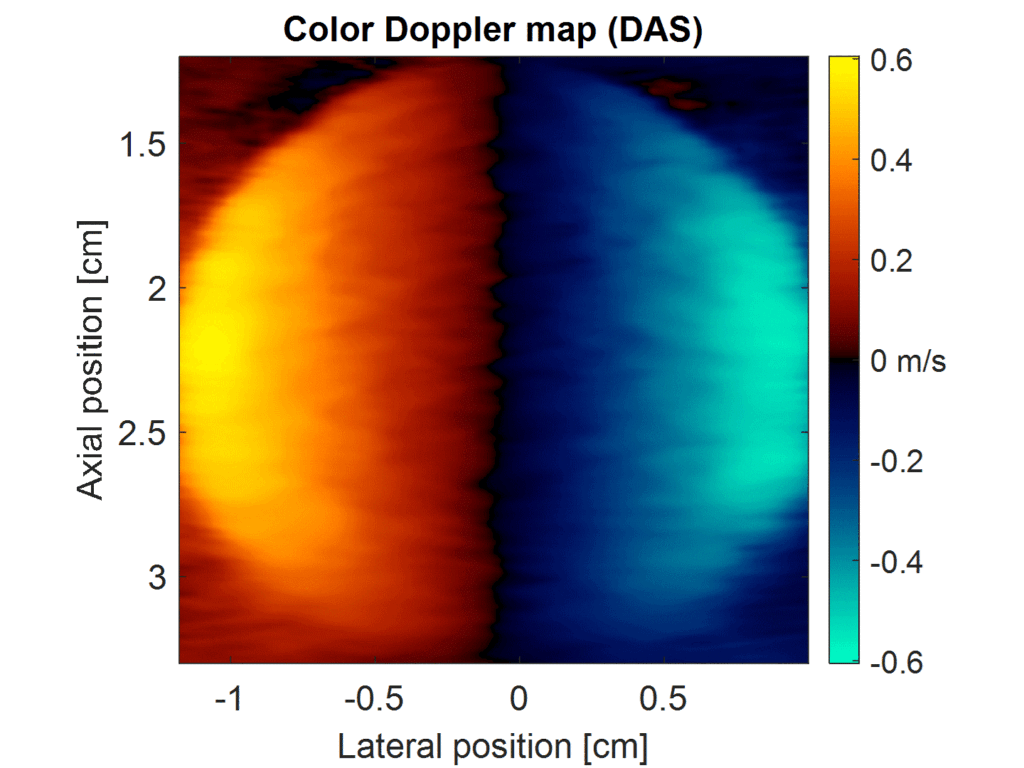
Results
Publications
- Madhavanunni A. N. and Mahesh Raveendranatha Panicker, “A Nonlinear High-Resolution Beamforming for Plane Wave Ultrasound Flow Imaging,” in Elsevier Computers in Biology and Medicine 147, 105686 (2022).
- “Madhavanunni A.N. and Mahesh Raveendranatha Panicker, “Directional beam focusing based dual apodization approach for improved vector flow imaging,” in Proc. of IEEE ISBI 2020, Iowa City, April 2020.
- “Madhavanunni A.N. and Mahesh Raveendranatha Panicker, “Triangulation based vector flow imaging with non-steered plane waves for transverse flows,” in Proc. of SPIE Medical Imaging 2020, Houston, Feb 2020.